What is financial technology – fintech?
Since the Digital Revolution, also known as the Third Industrial Revolution, the shift from analogue electronic technology towards digital electronics has begun and the Financial Technology, or FinTech, industry has evolved explosively.
The term “financial technology”, or in short “FinTech”, is broadly understood as the technology used to automate and improve the delivery of financial services. FinTech applies to any innovative way of how people transact business or perform financial activities such as money transfers, depositing a check with a smartphone, raising money to start a business, managing investments and much more. Today, some of the most active areas of FinTech innovation include:
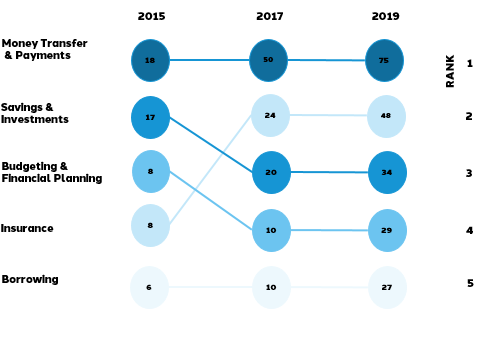
Comparison of fintech categories ranked
The FinTech industry is highly dynamic and innovative and new technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain will continue to spur the creation of new FinTech services. A study conducted by EY shows the development of FinTech services over time. In 2019, the most common used category is Money Transfer & Payments, as 75% of consumers use one or more services in this category. Particularly noteworthy is the strong adoption of insurance.
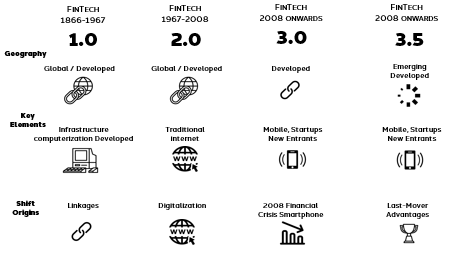
The evolution of fintech?
Digital innovation is disrupting and redefining financial services at a rapid pace. Nowadays, we think of FinTech in terms of cryptocurrencies, blockchain, and start-ups, however, the first groundbreaking developments happened much earlier and can be traced back to the late 19th century.
FinTech 1.0 is all about infrastructure
During the period 1866-1967, the financial globalization has started. In the beginning, technologies such as the telegraph, railroads, and steamships enabled the rapid transmission of financial information across borders for the first time. The first transatlantic cable (1866) and Fedwire (1918) in the USA enabled the first electronic fund transfer system using technologies such as telegraph and Morse code.
FinTech 2.0 is about the shift from analogue to digital
The second phase is introduced by the installation of the first ATM by Barclays in 1967 and marks the shift from analogue to digital. Various significant trends followed in the early 1970s, such as the establishment of the world’s first digital stock exchange, NASDAQ . During the 80s, we saw the rise of bank mainframe computers for data and book keeping and the 90s brought us the internet and early stage e-commerce.
FinTech 3.0 is about decentralization and web 3
The financial crisis soon escalated into a global economic crisis, with the public quickly developing a distrust of the traditional banking system. In 2008, a whitepaper published by Satoshi Nakamoto, revealed all the details of bitcoin technology. The entire bitcoin system is decentralised and the technology is fully disclosed. The invention of bitcoin in 2008 spurred the creation of many new cryptocurrencies that are commonly known as altcoins. Additionally, FinTech 3.5 incorporates emerging markets, as the countries with the highest FinTech usage are China (69%) and India (52%).